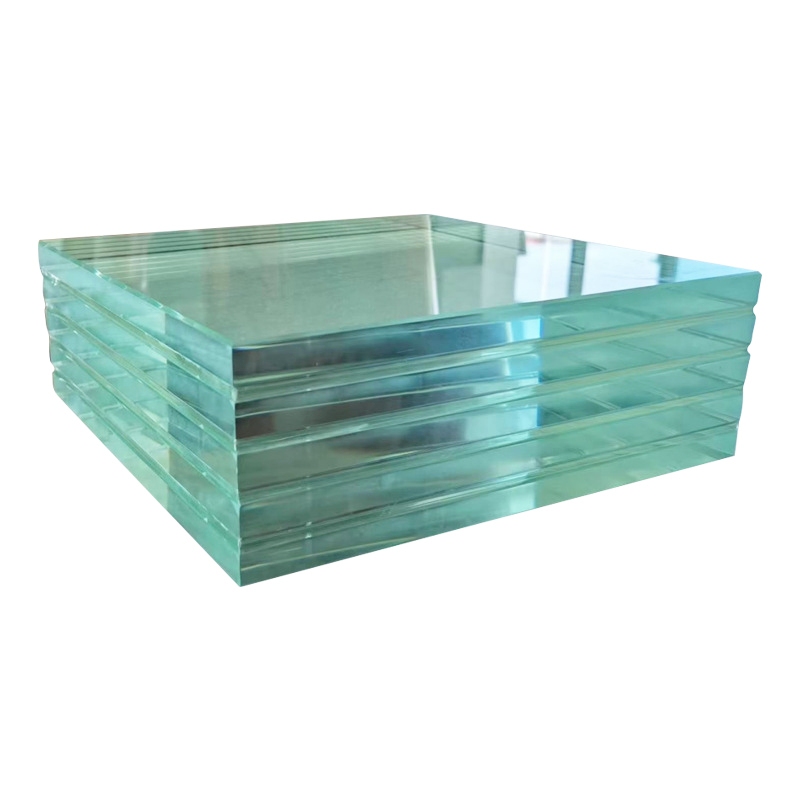
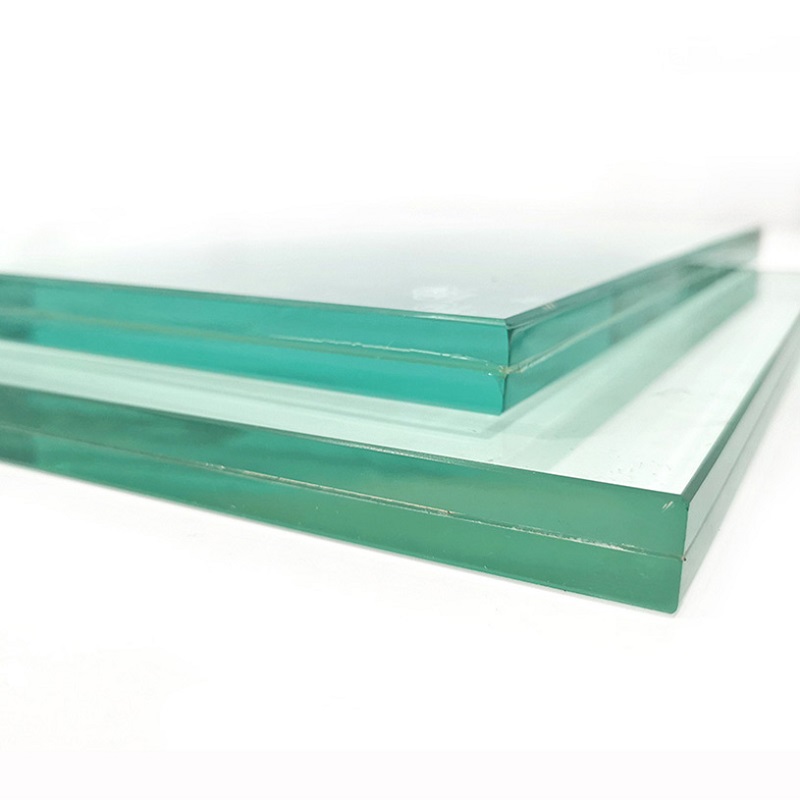
Tempered glass, recognized for its exceptional strength and safety features, has become indispensable across a spectrum of applications prioritizing safety and durability. From skyscraper windows to smartphone screens, tempered glass is a preferred choice where resilience is paramount. Innovations in tempered glass technology have made it an even more valuable material in modern construction and manufacturing.
The Tempering Process of Tempered Glass
Grasping the innovations in tempered glass requires understanding its fundamental tempering process. This involves heating standard annealed glass to a high temperature followed by a rapid cooling mechanism, or quenching. The swift cooling causes the exterior of tempered glass to solidify more quickly than its core, resulting in remarkable resilience and shatter resistance compared to untreated glass.

Strength and Longevity of Tempered Glass
Innovations in tempered glass technology have marked significant advancements in the formulation of stronger compositions and refinement of manufacturing methods. Advances in glass chemistry and production techniques have enabled manufacturers to create tempered glass with unprecedented levels of strength and longevity. This amplified durability positions tempered glass as a material of choice for safety-critical applications such as automotive windows, building exteriors, and furniture.
Furthermore, developments in surface treatments and coatings have enhanced the scratch resistance and longevity of tempered glass. Nanotechnology-based coatings can form a protective shield on the tempered glass surface, mitigating the risk of scratches and wear. These coatings also simplify the cleaning and maintenance process, thereby extending the lifespan and visual appeal of tempered glass.
Intrinsic Safety Properties of Tempered Glass
Beyond its inherent strength, tempered glass is engineered to fracture in a controlled pattern, reducing the risk of injury from breakage. Unlike regular glass, which can shatter into hazardous shards, tempered glass breaks into small, dull pieces, minimizing the potential for severe cuts and injuries. This safety feature is particularly valuable in environments where the risk of glass breakage is present, such as in entryways, barriers, and shower enclosures.
Innovations have fortified the safety aspects of tempered glass. Some manufacturers now integrate sensors within tempered glass that can identify cracks and structural issues in real time. These sensors can notify occupants or maintenance staff of potential dangers, facilitating prompt action and preventive measures.
Diverse Industry Applications of Tempered Glass
The improved safety and longevity of tempered glass have led to its broad acceptance across various industries. In the automotive sector, tempered glass is widely used for windscreens, side windows, and rear windows due to its impact resistance and shatterproof qualities. In construction, it is favored for windows, doors, and facades in high-rise structures where safety and robustness are non-negotiable.
Additionally, tempered glass is gaining popularity in the consumer electronics field, including smartphones, tablets, and touch screens. Its durability and resistance to scratches make it an optimal choice for safeguarding sensitive electronic displays from daily wear and tear.

Standardization and Quality Assurance for Tempered Glass
Ensuring the safety and dependability of tempered glass products is paramount, and this is achieved through stringent quality standards and testing protocols. Bodies such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have set guidelines governing the production and testing of tempered glass.
For example, ASTM International offers standards like ASTM C1048, which addresses heat-treated flat glass, and ASTM C1172, which pertains to laminated architectural glass. These standards lay out specifications for glass composition, strength, durability, and safety, assisting manufacturers in producing high-grade tempered glass that meets industry benchmarks.
Innovation and the Future of Tempered Glass
In summary, the evolution of tempered glass technology has transformed the design and construction of buildings, vehicles, and consumer products. With its improved strength, durability, and safety features, tempered glass remains a top contender for architects, engineers, and manufacturers globally. By adhering to rigorous quality standards and integrating new technologies, the tempered glass industry is set to continue its progress and ensure the ongoing safety and reliability of its products.





