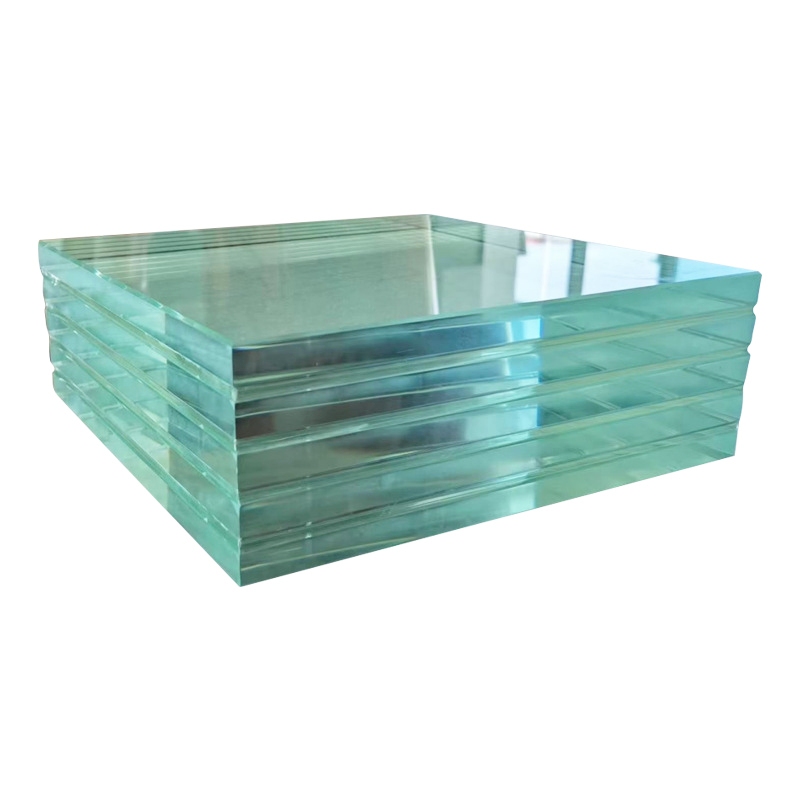
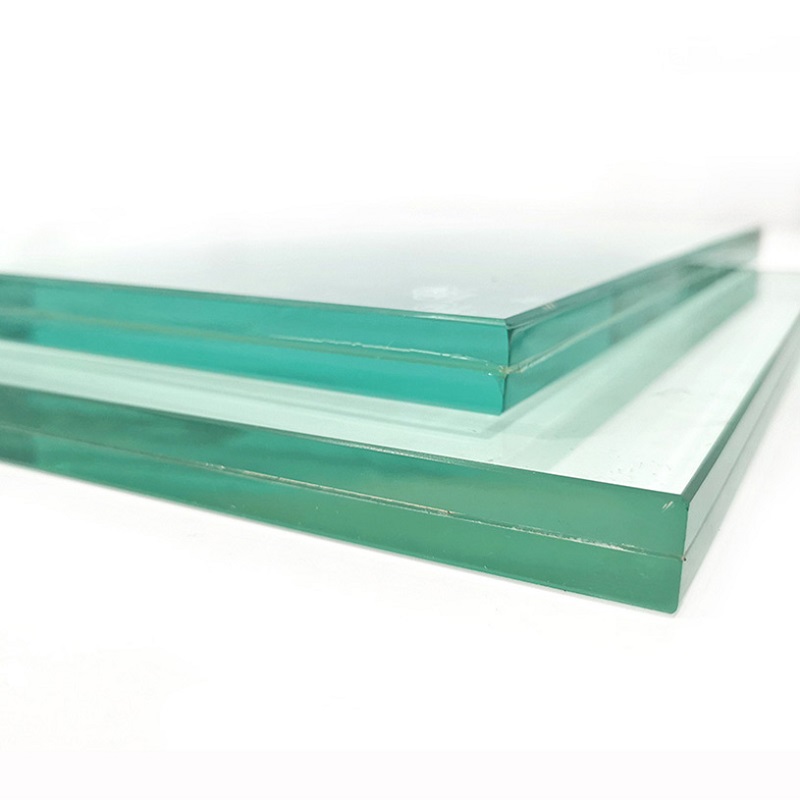
New Choice for Building Safety! A Comprehensive Comparison of EVA, PVB, and SGP Interlayer Films for Laminated Glass

In modern architecture, the application of laminated glass (also known as sandwich glass) is becoming increasingly widespread. From curtain walls to skylights, from railings to daylighting roofs, PVB glass and other types of laminated glass not only provide aesthetically pleasing visual effects but also serve critical safety functions. As a representative of safety glass, laminated glass relies heavily on its core material—the interlayer film—which directly impacts key performance indicators such as impact resistance, durability, and optical properties.
Currently, the mainstream interlayer films for laminated glass on the market primarily fall into three categories: EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer), PVB (polyvinyl butyral), and SGP (ionoplast interlayer). What are their respective characteristics? Which one better suits your architectural needs? This article will delve into a detailed comparison of their performance to help you make the best choice.
1. The Core of Laminated Glass: The Role of the Interlayer Film
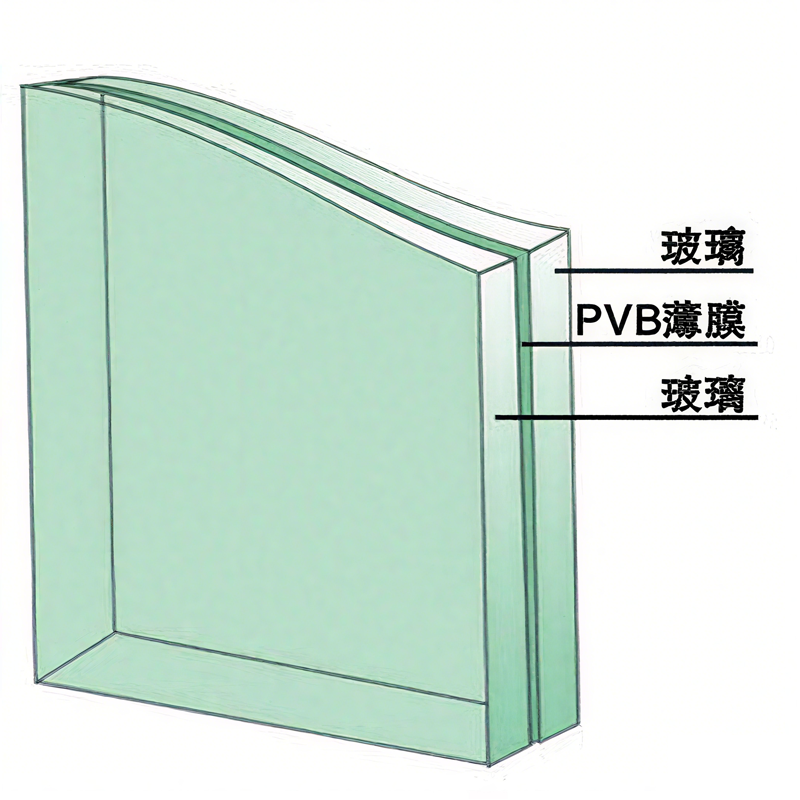
PVB glass and other laminated glass products are composed of two or more glass sheets bonded with a polymer interlayer film under high temperature and pressure. When the glass is impacted and shattered, the fragments adhere to the film, preventing them from scattering and causing injury, thereby enhancing safety. Additionally, laminated glass offers features such as sound insulation, UV protection, and explosion resistance, making it widely applicable in construction, automotive, and photovoltaic fields.
The performance of the interlayer film directly determines the laminated glass's:
Impact resistance (anti-smash, anti-explosion)
Weather resistance (UV resistance, anti-aging)
Optical performance (light transmittance, haze)
Bonding strength (adhesion between glass and film)
Construction convenience (processing temperature, technical requirements)
So, among PVB glass and other laminated glass products using EVA, PVB, and SGP films, which one stands out as the superior choice?
2. EVA Film: Cost-Effective but Limited Performance
Basic Characteristics
EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) is a thermoplastic material commonly used in photovoltaic module encapsulation and standard laminated glass.
Advantages
✅ Low cost: Priced lower than PVB and SGP, suitable for budget-conscious projects.
✅ Simple processing: Can be produced using a one-step vacuum method without requiring an autoclave, making it suitable for small-scale manufacturers.
✅ Good light transmittance: High initial light transmittance, ideal for decorative glass and furniture glass.
Disadvantages
❌ Weak impact resistance: Prone to delamination upon impact, unsuitable for high-safety applications.
❌ Poor weather resistance: Susceptible to yellowing and aging under prolonged UV exposure.
❌ Low bonding strength: Glass fragments may detach upon breakage, offering lower safety compared to PVB glass and SGP laminated glass.
Ideal Applications
Indoor decorative laminated glass (e.g., furniture, partitions)
Low-safety alternatives to PVB glass
Photovoltaic module encapsulation
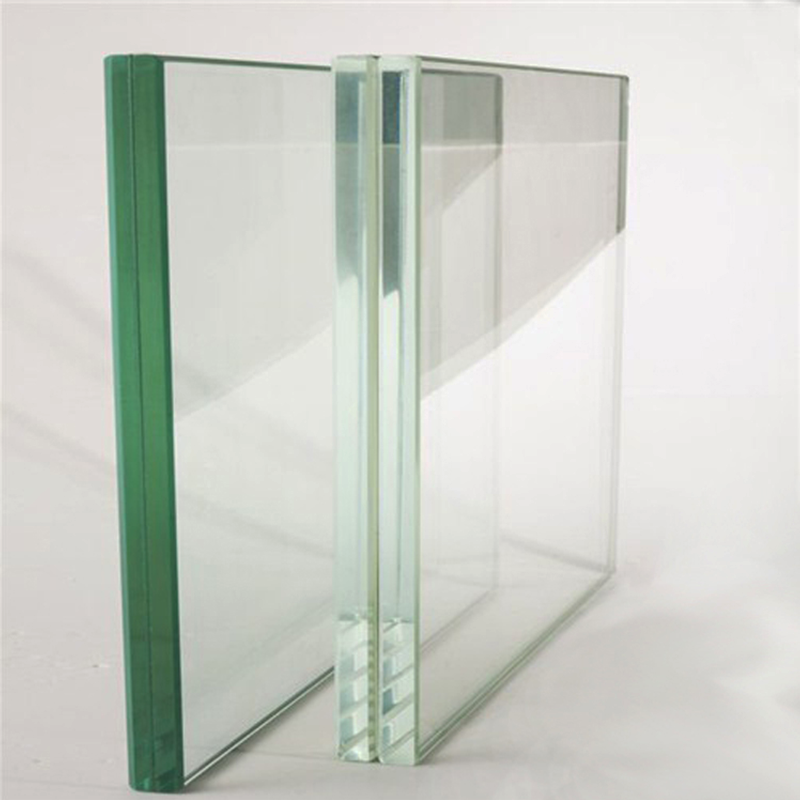

3. PVB Film: Market Leader, Balancing Safety and Weather Resistance
Basic Characteristics
PVB (polyvinyl butyral) is currently the most widely used interlayer for laminated glass, accounting for over 70% of the market share.
Advantages
✅ High safety: Strong impact resistance; even when shattered, glass fragments remain adhered to the film, meeting anti-explosion standards.
✅ Excellent weather resistance: UV-resistant and anti-aging, with a service life of up to 20 years.
✅ Effective sound insulation: The damping properties of PVB glass significantly reduce noise, making it suitable for street-facing buildings.
✅ Good flexibility: Can be used for curved glass, ideal for unconventional architectural designs.
Disadvantages
❌ High processing requirements: Must be produced using an autoclave, with complex techniques that small factories may struggle to master.
❌ Prone to delamination in humid environments: If edges are not properly sealed, moisture ingress may cause separation.
❌ Slightly lower light transmittance: Compared to EVA and SGP laminated glass, PVB film may exhibit slight yellowing, affecting clarity.
Ideal Applications
Architectural curtain walls, skylights, and other laminated glass applications
PVB glass for anti-explosion facilities in banks, jewelry stores, etc.
Automotive windshields
High-acoustic-demand venues (e.g., concert halls, airports)
4. SGP Film: High-Performance Leader, Far Exceeding PVB
Basic Characteristics
SGP (SentryGlas Plus, DuPont’s ionoplast interlayer) is a new high-performance laminated glass interlayer that uses ionomer technology, offering strength far surpassing traditional PVB glass.
Advantages
✅ Exceptional strength: Tear resistance is five times that of PVB glass, maintaining structural integrity even when shattered. Suitable for bulletproof glass and buildings in typhoon-prone areas.
✅ High penetration resistance: Effectively withstands extreme impacts like hurricanes and explosions.
✅ Superior weather resistance: Minimal yellowing, maintaining high light transmittance over long-term use.
✅ Excellent edge stability: Less affected by moisture, ideal for high-rise buildings and coastal laminated glass applications.
Disadvantages
❌ High cost: Priced 2-3 times higher than PVB glass, reserved for premium projects.
❌ Challenging processing: Requires specialized equipment and highly precise production techniques.
Ideal Applications
Curtain walls for super high-rise buildings
Bulletproof glass for military and banking (an upgrade over PVB glass)
Typhoon- and earthquake-prone regions
Large-span glass structures (e.g., glass walkways, glass bridges)
5. Comprehensive Comparison: EVA vs. PVB vs. SGP
| Performance | EVA Laminated Glass | PVB Glass | SGP Laminated Glass |
| Impact Resistance | Weak | Strong | Extremely Strong |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Outstanding |
| Light Transmittance | High | Moderate | High |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Excellent | Good |
| Price | Low | Moderate | High |
| Ideal Applications | Decorative Glass | Architectural Curtain Walls | Super High-Rise Buildings |
6. How to Choose the Right Laminated Glass Interlayer?
Standard buildings, limited budget → PVB glass (cost-effective, sufficient safety)
Premium buildings, extreme environments → SGP laminated glass (superior impact resistance, ideal for typhoon-prone areas and anti-explosion needs)
Decorative use, low safety requirements → EVA laminated glass (low cost, easy processing)
7. Future Trends: High-Performance Films Will Dominate
As building safety standards rise, PVB glass will remain the market leader. However, high-performance laminated glass like SGP will see increased adoption in super high-rise buildings and extreme climate regions. Meanwhile, new composite materials (e.g., TPU, PC) are under development, potentially offering lighter, stronger, and more durable laminated glass solutions in the future.
Conclusion
EVA laminated glass, PVB glass, and SGP laminated glass each have their pros and cons. The choice of interlayer depends on safety requirements, budget, and environmental factors. For standard buildings, PVB glass offers the most balanced solution, while for super high-rise buildings and anti-explosion scenarios, SGP laminated glass’s exceptional performance justifies the investment. We hope this article helps you make a more informed decision!
PVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glassPVB glass





